Understanding Measles: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
1. Definition of Measles
Measles is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the measles virus. It primarily affects children but can occur in individuals of any age. Measles is characterized by a distinctive red rash, fever, and respiratory symptoms. The disease can lead to severe complications, especially in young children and immunocompromised individuals.
2. Causes of Measles
Measles is caused by the measles virus, which spreads through:
- Respiratory droplets: When an infected person coughs or sneezes, tiny droplets containing the virus can be inhaled by others.
- Direct contact: Touching surfaces contaminated with the virus can also result in infection.
- Highly contagious: Measles is extremely contagious, with a 90% infection rate among non-immune individuals exposed to the virus.
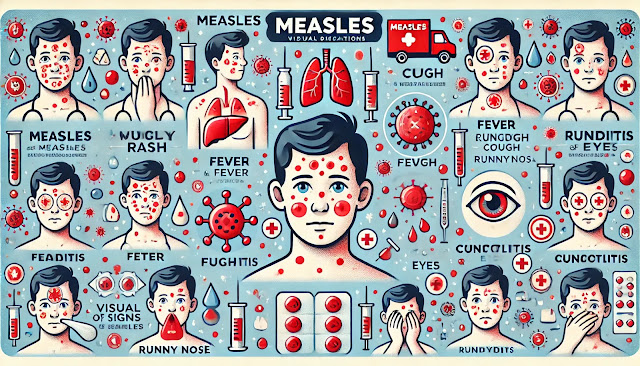
3. Symptoms of Measles
Symptoms typically appear 10-14 days after exposure and include:
- Red rash: Starting on the face and neck, spreading to the body.
- Fever: Often high, around 40°C (104°F).
- Cough: A dry, persistent cough.
- Runny nose: Accompanied by cold-like symptoms.
- Conjunctivitis: Red, watery eyes.
- Koplik’s spots: Small white spots inside the mouth, appearing early in the infection.
4. Diagnosis of Measles
Measles is diagnosed through:
- Physical examination: A doctor can recognize the characteristic rash and Koplik’s spots.
- Blood tests: These can confirm the presence of measles antibodies or the virus itself.
- Throat or nasal swabs: Samples may be tested to detect the virus.
5. Treatment of Measles
There is no specific antiviral treatment for measles, but supportive care can help manage symptoms:
- Rest and hydration: Bed rest and plenty of fluids are essential.
- Fever reducers: Medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help lower fever and relieve discomfort.
- Vitamin A: In some cases, high doses of vitamin A are given to reduce the risk of complications, especially in children.
6. Prevention of Measles
The most effective way to prevent measles is through vaccination:
- MMR vaccine: The measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles.
- Herd immunity: Widespread vaccination protects those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants or individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Isolation: Infected individuals should be isolated to prevent spreading the virus.
Conclusion
Measles is a highly contagious disease that can lead to serious complications if not prevented through vaccination. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and preventive measures is crucial to controlling its spread. This blog provides general information, but please consult a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.


.%20The%20image%20should%20depict%20a%20human%20figure%20from%20.webp)

%20where%20a%20person%20stands%20with%20their%20knees%20touching%20while%20their%20feet%20remain%20apart,%20creating%20an%20'X'.png)


%20in%20a%20medical%20context.%20The%20image%20should%20show%20an%20anatomical%20view%20.webp)

Comments
Post a Comment